World
What is a presidential pardon and how has it been used in the US?
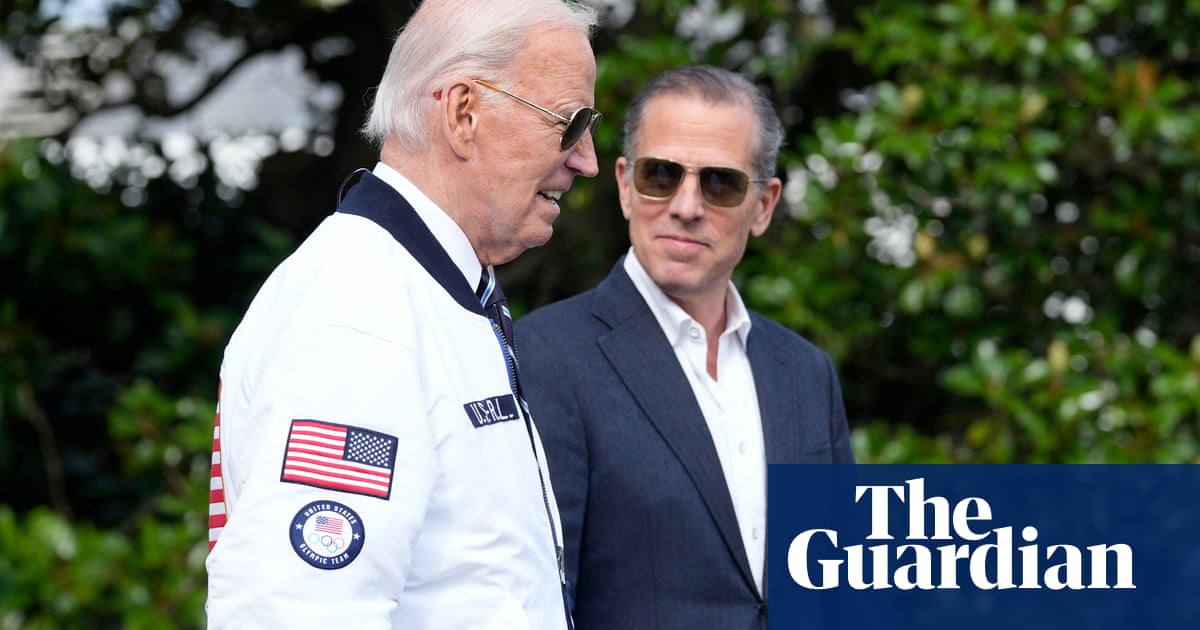

Joe Biden’s decision to pardon his son Hunter on Sunday for any federal crimes “he committed or may have committed” between 1 January 2014 and 1 December 2024 has brought renewed focus on the expansive power the US constitution gives the president to grant official clemency.
It’s a power that presidents have deployed since George Washington, who pardoned those involved in the Whiskey Rebellion, to Donald Trump, who pardoned his political allies.
What is the pardon power?
The presidential pardon power is explicitly outlined in the US constitution.
Section 2 of article II says that the president has the power to “grant Reprieves and Pardons for Offences against the United States, except in Cases of Impeachment”. The president’s power only applies to federal crimes, not state ones. It also does not apply to cases of impeachment.
The founders took the pardon power from England, where there was a longstanding tradition of the king’s ability to issue mercy pardons. There was some debate about whether Congress should be required to give approval of pardons and whether there should be an exception for treason, but Alexander Hamilton pushed the constitutional convention to include a broad pardon power solely vested in the president.
“As men generally derive confidence from their numbers, they might often encourage each other in an act of obduracy, and might be less sensible to the apprehension of suspicion or censure for an injudicious or affected clemency. On these accounts, one man appears to be a more eligible dispenser of the mercy of government, than a body of men,” he wrote in Federalist no 74, one of a series of essays to promote the ratification of the constitution.
When it came to treason, he argued that the president could deploy the pardon power as a tool to negotiate and unify the country. “In seasons of insurrection or rebellion, there are often critical moments, when a welltimed offer of pardon to the insurgents or rebels may restore the tranquillity of the commonwealth; and which, if suffered to pass unimproved, it may never be possible afterwards to recall,” he wrote.
Bernadette Meyler, a law professor at Stanford University who studies British and US law, described it as “the one emergency power written into the constitution, other than the suspension of habeas corpus.
“It’s one thing that is a concession to the idea that there might be certain unforeseen circumstances that the president would have to intervene in,” she said. “It goes along with the president’s control also over the army and navy and military power because, in the context that it was being contemplated, it was really being thought about as another tool within the ability to control domestic unrest.”
How has the pardon power been used?
George Washington issued the first pardons in 1795 to two men who were involved in the Whiskey Rebellion, a violent uprising in Pennsylvania to protest a tax on whiskey and other alcohol products by the nascent federal government.
A key moment in the pardon power came after the civil war, when president Andrew Johnson issued “a full pardon and amnesty” to any person “who, directly or indirectly, participated in the late insurrection or rebellion” during the civil war. This and similar pardons around the same time led the US supreme court to interpret the pardon power to allow the president to grant broad amnesty to a group of people and not just for specific crimes already committed, Meyler said.
After Richard Nixon resigned the presidency in the 1970s after Watergate, Gerald Ford issued a full and unconditional pardon for any crimes.
In 1977, Jimmy Carter issued a mass pardon for those who had dodged the draft for the Vietnam war. At the end of his term in 1992, George HW Bush pardoned six people involved in the Iran-Contra affair, including the former defense secretary Caspar Weinberger.
In his last day in office in 2001, Bill Clinton pardoned his half-brother and gave an extremely controversial pardon to Marc Rich, a fugitive convicted of financial crimes whose ex-wife had been a major donor to Democrats and the Clinton campaign.
Barack Obama granted clemency to more than 1,700 people while in office, including hundreds who had been convicted of non-violent drug offenses.
Who did Donald Trump pardon?
Trump did not hesitate to use the pardon power during his presidency to help political allies. He pardoned Charles Kushner, the father of his son-in-law Jared. The elder Kushner had pleaded guilty years earlier to tax evasion and witness tampering (Trump has now tapped him to be ambassador to France).
He pardoned his political adviser Steve Bannon, who faced charges of defrauding donors on a charity related to building a wall at the southern border. He also pardoned Paul Manafort, who served as a top official on his 2016 campaign, and Trump ally Roger Stone.
Trump pardoned the former New York City police commissioner Bernard Kerik, the conservative personality Dinesh D’Souza, and Elliott Broidy, a major Republican donor. He also pardoned the rapper Lil Wayne and Alice Marie Johnson, a woman who had spent decades in prison for drug offenses but earned considerable attention after Kim Kardashian took on her cause.
Trump has said he will issue a mass pardon for those involved in the January 6 attacks, a move that would end years of work by the justice department to investigate and criminally prosecute those involved in the attacks.
Do other countries have a pardon power?
The power to pardon is one that widely exists around the world, said Andrew Novak, a professor at George Mason University who is the author of Comparative Executive Clemency: The Constitutional Pardon Power and the Prerogative of Mercy in Global Perspective.
But the United States is somewhat unique in allowing its chief executive the ability to pardon without having to get input or sign-off from others.
“Biden can grant a pardon without input from anybody, which is much more of like a medieval English king conception of the pardon power, which is kind of ironic,” he added. “We have kind of an old-fashioned conception of the pardon power, at least generally.”
“Having this unlimited pardon power that’s more similar to like 1700s England than it is to the current state of affairs in the western world,” he added. “In most countries in Europe, and the comparators in the developed world, they require input from someone else.” That requirement for input, Novak said, can somewhat limit a pardon being used to serve political or personal interests, the way it can be used in the US.
Many countries also don’t allow for a pardon before conviction, Novak said, and there has been a movement over the last few decades in other countries for more transparency to ensure that proper processes are followed.
About half of constitutions around the world limit the pardon power to something that can only occur after conviction, are only for specified offenses, or require an executive to consult others, Novak said. It’s uncommon for countries to have a ban on self-pardoning or pardoning a family member, he added.
“Maybe it’s not common because the circumstance doesn’t arise very often,” he said. “The pardon power has always been a corruption risk going back to medieval times and can be used for many forms of self-dealing, like shielding one’s close associates or supporters.”
The US founders understood impeachment to be an important check on the pardon power, Meyler said. “As we’ve seen it’s extremely hard to actually convict on an impeachment so that has proved to be really a fictional limitation on the president’s power.”